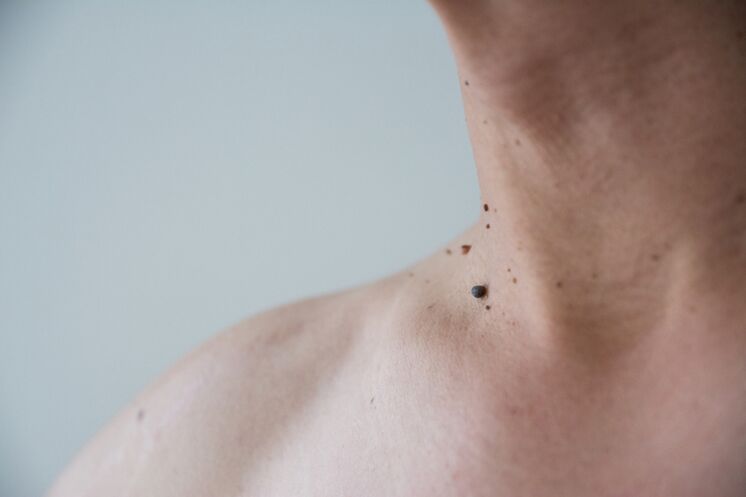
There are very few people who would not face such a problem as warts on the body. These growths can occur on the body in young people, adults and the elderly. Usually, warts are just a cosmetic problem that degrades a person's appearance. And only in rare cases do these formations pose a real threat to health.
What is a wart?
Our skin has a smooth surface. In some cases, however, there may be prominent skin growth on it. They are called warts. Usually these are permanent formations that do not change for many years.
The mechanism of appearance of warts is the growth of the top layer of the skin. The size of the formations varies from 1 mm to several centimeters. This parameter depends on the type of formation and its location on the skin. Fusion of several warts is often observed. The color of the skin growths is usually flesh, but they can take other shades, such as pink or brown.
Medicine classifies warts as benign tumors. They do not grow and do not penetrate into the surrounding tissue.
In the international classification of diseases, the following codes are assigned to warts:
- B07 - viral warts,
- A63. 0 - genital warts,
- L82 Seborrheic Keratoma
Most warts are viral, sexually transmitted warts are gendered, and seborrheic keratomas are senile warts that are not contagious.
The following skin lesions should be distinguished from warts:
- nevi (mol),
- calluses,
- malignant tumors,
- basal cell carcinoma,
- broad warts due to syphilis.
Some of these formations can be life threatening. Therefore, if suspicious formation occurs on the body, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Why do warts occur?
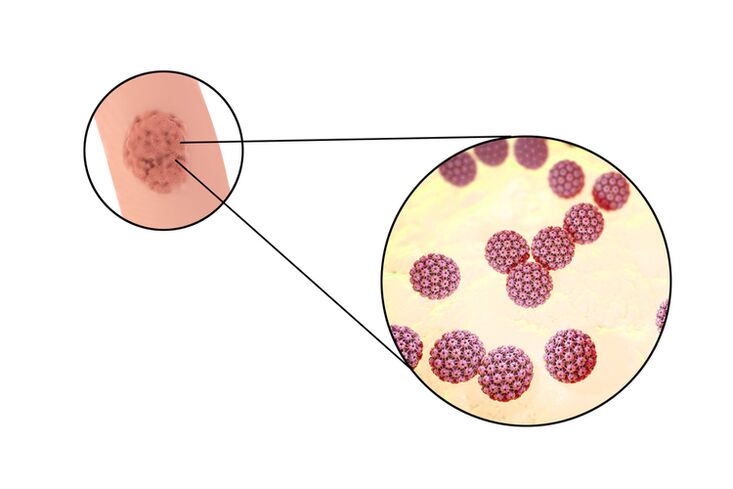
Usually a viral infection is the cause of warts. The process of appearance of warts is as follows. The human papillomavirus enters the skin cells and causes them to divide rapidly. As a result, a growth or papilloma develops on the skin. However, there are types of warts that the virus has nothing to do with.
Strictly speaking, papillomas do not always occur on the skin. Often these formations are found on the mucous membranes, inside the bladder, in the larynx, on the cervix, etc. However, it is customary to call warts only papillomas that appear on the skin.
Warts can be placed on any part of the body. However, some species have their favorite places. For example, warts usually form in the groin and anus; acrochords prefer skin folds in the upper body.
The human papillomavirus does not multiply outside the body. However, it can last for a long time in hot and humid places. Therefore, people can often get infected with it when they visit baths, saunas, swimming pools. But the virus does not live long in the open - it is neutralized by the sun's ultraviolet radiation.
According to studies, approx. 80% of the world's population is infected with some form of human papillomavirus. There are a total of two hundred strains of these viruses. Some viruses are relatively harmless, others lead to papillomas, and others can even cause malignant tumors. Some strains can be transmitted from person to person. Therefore, certain types of warts can be contagious. But the transmission of the disease from frogs and amphibians as well as from other representatives of the fauna, contrary to popular belief, is impossible. This is explained by the fact that expensive papillomaviruses do not multiply in the human body.
You can be infected with a new type of virus through personal contact, hand-sharing, sharing household items (such as towels) when visiting public places (swimming pools, baths, saunas, transportation), through small wounds, and sexually.
The papillomavirus that has entered the body does not always cause the appearance of the disease. Usually, factors associated with the disease are stress, impaired immunity (for example, due to infectious diseases). At the same time, the virus can remain in the body for several years and wait in the wings.
Variants of warts
Doctors distinguish between different types of warts:
- common (vulgar),
- youthful (flat),
- pointed (condyloma),
- senile,
- wire-like.
Birthmarks (nevi) should be distinguished from these types of warts. Normally, birthmarks do not protrude from the surface of the skin and are dark in color, although there are exceptions.
Vulgar warts
This type of wart occurs in 70% of cases. It is caused by papillomavirus. Externally, vulgar (ordinary) papillomas look like small semicircular formations on the surface of the skin. They are usually completely painless. The size of the formations is from several mm to 1 cm. Their surface is usually uneven, uneven and often resembles the surface of the cauliflower. Color - flesh-colored, grayish, yellow-brown. Frequent localizations - hands, face, fingers, lips, knees, elbows. Mucous membranes are rarely affected.
Often, ordinary papillomas can disappear on their own. The peculiarity of this type of papilloma is that they often grow not individually, but in groups. You can often find a large papilloma around which small ones grow. If you remove the largest (maternal) papilloma, the small ones usually disappear.
Common papillomas can occur at any age. They often occur in school-age children.
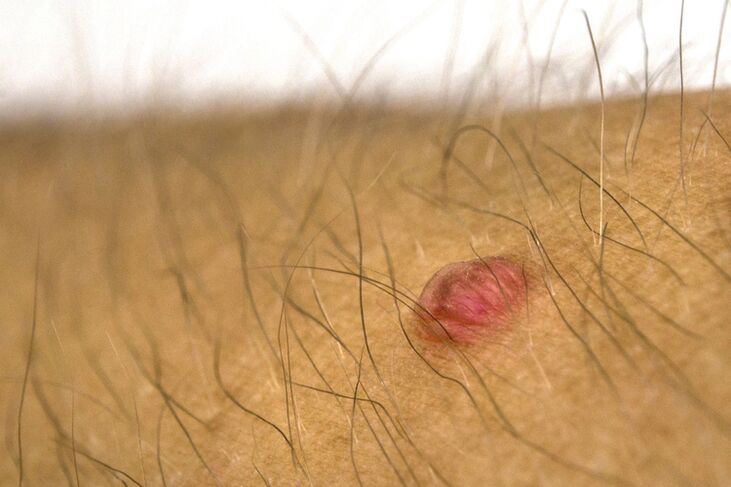
Teenage warts
This type of papilloma usually occurs in children and adolescents. But in people of mature age, they can also show up. These papillomas are also often called flat papillomas. They account for only 4% of all warts.
They can often be found at hand. They can also be observed on the feet and face, close to the nails, between the toes, on the legs and on the neck. They are often associated with hormonal changes in the body. Like ordinary papillomas, they do not pose a significant danger and can go away on their own. They do not usually cause physical discomfort, but they can worsen the appearance.
Flat papillomas are usually flesh-colored and protrude only slightly beyond the skin surface (approximately 1-2 mm). They can reach a diameter of 5 mm, but they are usually smaller than vulgar. Flattened papillomas can occur near wounds and cuts. Juvenile papillomas usually have a smooth surface and uneven, albeit well-defined borders. Due to the lack of a stratum corneum on the surface, they may appear shiny.
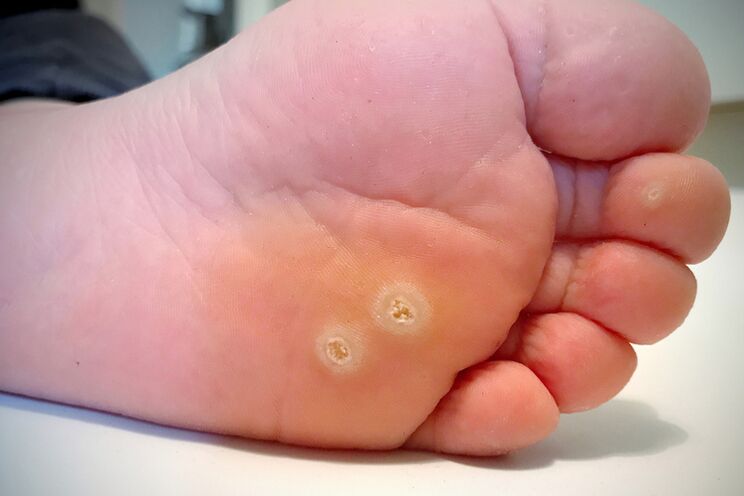
Plantar warts
This is an extremely unpleasant type of skin growth that occurs on the feet. Sometimes they are confused with grains. However, plantar papillomas have a feature that distinguishes them from corn. If a plantar wart is damaged, it will usually bleed. For cereals, this phenomenon is not typical. Although on the outside, papillomas on the legs may look like calluses - they are usually hard and keratinized. Their color is usually dirty gray, dark or dirty yellow with a brown tint. Black dots may appear on the surface.
Often a plantar wart is found on the leg. But they can also meet in groups and grow together. Plantar papillomas grow not only outside the skin but also deeper.
On the outside, warts of this type may look common. They usually have a semicircular shape. However, if a person is constantly developing such a skin formation, it may assume a flat shape.
The appearance of papillomas on the soles has little to do with age; they can occur in both young and old. These formations can also be observed in children.
Plantar papillomas can cause discomfort and even severe pain when walking. When you step on such an outgrowth, it looks like you are stepping on a small rock. Outwardly, warts can sometimes look like thorns. That is why people call these types of papillomas spines.
In a calm state, these formations can cause itching. Like other types of papillomas, plantar warts develop under the influence of papillomavirus. The virus often gets on the skin of the feet from the environment. For example, it is not uncommon to catch this virus by visiting a pool without rubber shoes. Uncomfortable shoes also contribute to the occurrence of skin lesions as they often occur in places where shoes rub the feet. Severe sweating and inadequate foot hygiene are also contributing factors.
It is not recommended to touch the papillomas on the sole with your hands, as this way you can transmit the virus to other areas of the skin.
Plantar warts treatment
Sometimes papillomas of this type can disappear on their own. This happens in about half of the cases. But sometimes it takes a long time to wait for this moment and not everyone can afford it, especially if the education feels painful. If an outgrowth on the foot causes a sharp pain, does not allow to walk, it must be removed. In addition, education of more than 1 cm must be removed. The removal operation can only be performed at the doctor's office.
If there is any doubt that the formation on the leg belongs to any kind of papilloma, the doctor can perform a number of diagnostic procedures. These include scraping and analysis of the stratum corneum, PCR analysis for the presence of the papillomavirus genome. To determine the formation and the size of the formation, an ultrasound scan is performed. Warts on the leg require different diagnosis from syphilis warts. However, comprehensive diagnostic measures are not usually performed as it is not difficult to diagnose papilloma on the leg.
Sometimes medication can be tried to remove a growth on the foot. For the removal of warts, preparations with salicylic acid, necrotizing agents, freezing aerosols and special plasters are suitable. However, removal with medication is usually not a quick procedure. You can quickly remove a wart on the sole using only tools available in medical institutions. These can be methods:
- laser,
- surgical,
- electrocoagulation,
- cryodestruction,
- radio wave.
Each type of procedure has its own advantages and disadvantages. The surgical method is used, for example, mainly for large skin growths, as it severely damages the skin.
Genital warts
This is a special type of wart. They are usually found in the genital area. Their shape is also unusual as they look like papillae (hence their name). However, warts can also have an irregular shape that resembles cauliflower or rooster comb. The viruses that cause this type of warts are usually sexually transmitted. Condyloma can also be observed on the mucous membranes of the anus. Therefore, such warts are often called anogenital or genital organs. Less commonly, condyloma is found in the armpits of women below the mammary glands. Warts are flesh to pink. Sometimes several genital warts can grow together. Condyloma of this kind can also grow to large sizes. Warts can cause painful sensations during intercourse, defecation. If they are injured, they can bleed. Women with genital warts can also develop cervical cancer.
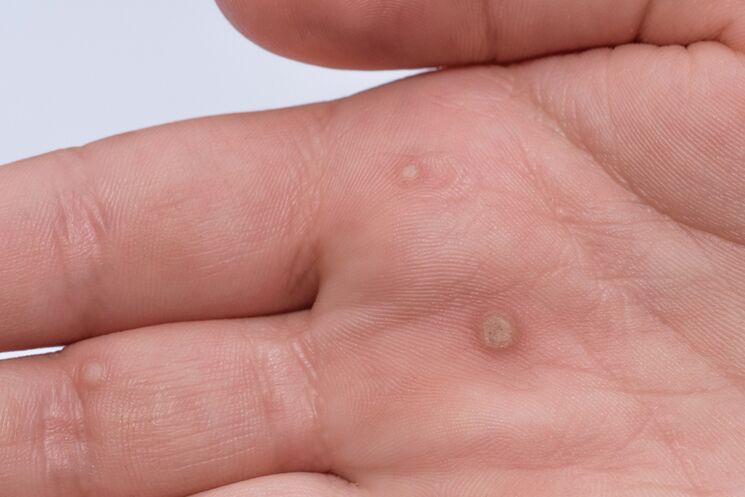
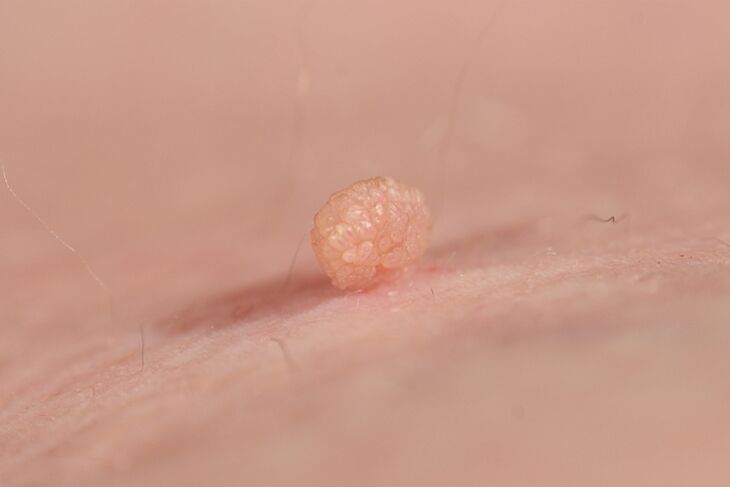
Filiform warts
This type of wart is extremely common. Filiform warts or acrochords often grow in large groups. Prefers acrochords for areas with thin skin. This is the area with the armpits, neck, shoulders, eyelids, nose wings. May occur in the groin, under the mammary glands in women. They usually do not bother a person and do not hurt, but they can itch.
Externally, filamentous warts resemble long threads. However, acrochords are often found that have a thin filiform stem to which a thick body is attached, usually spherical or hemispherical. They are also filiform. Such warts are called drooping.
Most warts of this type range in size from 1 mm to 5 mm. There are also acrochords larger than 1 cm. Sometimes several filamentous warts grow together.
Acrochords are rare in children. They are typical of people over the age of 35. And over the years, the number usually increases. Among people over the age of 70, this type of warts is observed in 100%. The tendency to have a large number of acrochords on the body can also be inherited. Acrochords are often associated with being overweight. In women, they can occur during pregnancy.
Filamentous warts have an unpleasant function. If a filamentous wart is torn off, a new one will soon grow instead. Acrochords rarely surpass themselves. Their appearance is promoted by increased sweating, decreased immunity.
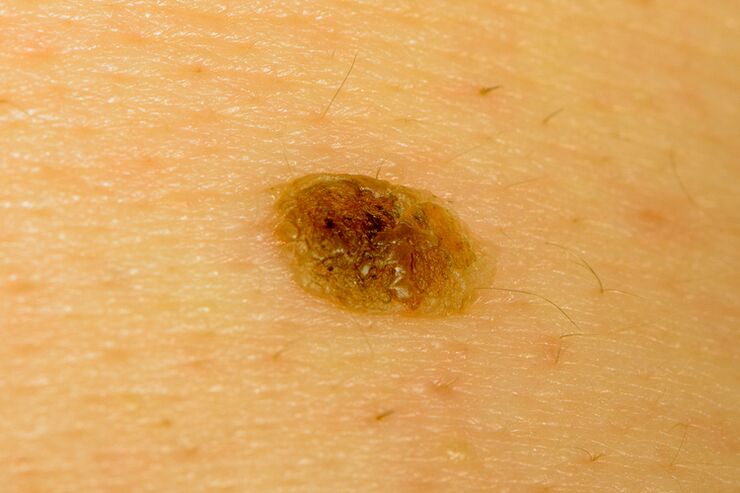
Senile warts
This type of wart has another name - seborrheic keratoma. It usually occurs in people over 60 years of age. Unlike other types of warts, senile keratomas are not caused by the human papillomavirus. The exact causes of their occurrence have not been determined. Keratomas are most likely associated with age-related changes in the body. They develop from the basal layer of the epidermis, which is why they are often called basal cell papillomas. Although this is not the real name because genuine papillomas are only caused by viruses. Heredity plays a significant role in the emergence of these neoplasms. Senile keratomas can often resemble melanoma. Therefore, if they occur, it is necessary to consult a doctor so that he can diagnose. However, senile keratomas usually do not require treatment and do not turn into malignant tumors.
On the outside, keratomas look like pink or yellow papules with a thickness of 1-2 mm. Their size ranges from 2 mm to 3 cm. Occasionally warts of this type reach a size of 4-6 cm. Keratomes have a fat, easily removable crust. Their surface is uneven, as if it were corrugated cardboard. As they grow up, keratomas often become like a fungal cap and their color changes to black or dark brown. Their surface becomes hard, they can crack.
Most often, keratomas are located on the neck and chest. Can be observed in groups. They appear less frequently on hands and face. They are not found on the mucous membranes. Usually there are no more than 20 keratomas on the body. If a person has many senile warts, this is often due to hereditary factors.
Senile keratomas do not disappear on their own. People with excessive amounts of seborrheic keratomas on the body are advised to increase the amount of vitamin C in their diet to prevent new growths. You should also avoid exposure to direct sunlight, overheating, hypothermia, stress.
Treatment
Most papillomas do not pose a serious threat. But after injury, they can hurt, soft. Then there is a risk of developing malignant tumors. Although in papillomas and keratomas, the risk of malignant transformation is much lower than in moles.
Papillomas are usually treated by removal (surgically using cold, high-frequency electric current or laser). Therapeutic treatments are usually less effective.
The indication for removal is tenderness in the skin formation, its large size, bleeding, deformity, placement in an uncomfortable place (for example, on the tip of the toe, on the soles, in the genital area), aesthetic considerations. Warts can also be removed.














































































